A thread is a lightweight sub process, a smallest unit of processing. It is a separate path of execution.
Threads are independent, if there occurs exception in one thread, it doesn't affect other threads. It shares a common memory area.
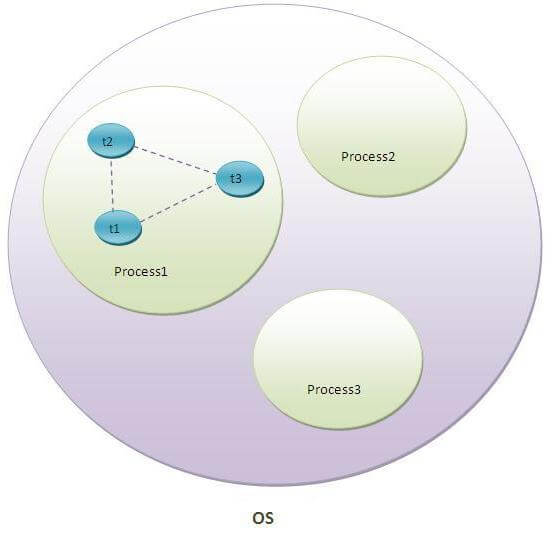
Thread is executed inside the process.
Thread life cycle
Ways of creating threads in java

Example 1,
Implements Runnable interface,
class MyThread implements Runnable
{
public void run()
{
System.out.println("concurrent thread started running..");
}
}
class MyThreadDemo
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
MyThread mt = new MyThread();
Thread t = new Thread(mt);
t.start();
}
}
Output : concurrent thread started running..
By Extending Thread class,

class MyThread extends Thread
{
public void run()
{
System.out.println("Concurrent thread started running..");
}
}
classMyThreadDemo
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
MyThread mt = new MyThread();
mt.start();
}
}
Output : concurrent thread started running..
Note on creating threads,

Using the
Thread class directly has the following disadvantages.- Creating a new thread causes some performance overhead
- Too many threads can lead to reduced performance, as the CPU needs to switch between these threads.
- You cannot easily control the number of threads, therefore you may run into out of memory errors due to too many threads.
No comments:
Post a Comment